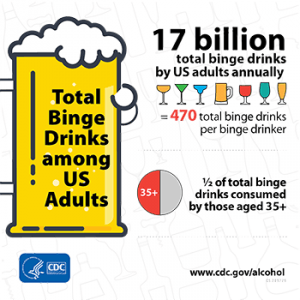ARTICLE SUMMARY: Is a friend or a loved one experiencing alcohol problems? Are you looking for a way to understand his/her behavior? This article gives you the basics on alcohol addiction. If you want to get deeper inside the mind of an alcoholic, this is a good place to start.
TABLE OF CONTENTS:
- What’s The Big Deal?
- The Secret of the Alcoholic Mind
- Is Alcoholism Treatable?
- Obstacles to Treatment
1. Being In Denial
2. Lack Of Devotion And Commitment
3. Lack Of Good Aftercare Plan - Top 5 Things To Avoid
- Extra Tip
- Your Questions
First, What’s The Big Deal?
The Big Deal about alcohol is that it negatively affects about 8% of the adult population in the U.S. Over consumption is one of the leading causes of preventable death. And alcohol is associated with a growing list of really bad diseases of the body and mind.
So, how did your loved one become addicted to it in the first place?
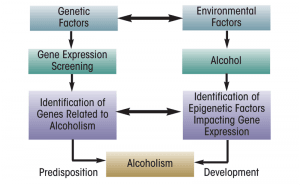
It might be consoling to know that a certain population of people have and will always be prone to alcoholism. Alcohol has played a significant part in religious, cultural and social practices in many societies. As it became rapidly produced and distributed, alcohol became one of the widely spread and most available substances across the world. This mass production of alcohol lead people to start using it more frequently, leading them from casual users, to abusers, and eventually people dependent on its psychoactive effects.
About 17.6 million people, or one in every 12 adults, suffer from alcohol abuse or dependence, which means that these individuals have lost control over their alcohol consumption.
And as we mentioned earlier, alcohol consumption impacts both the incidence and course of and the course of many health conditions. According to the World Health Organization, 5.9 percent of all global deaths in 2012 were caused by alcohol consumption. The Big Deal is that alcohol is legal…but it’s not going away. How can you help your loved one? What understanding do you need to have?
The Secret Of Getting Into An Alcoholic’s Mind
The secret of getting into an alcoholic’s mind is to understand how alcohol affects the brain. Both moderate and heavy drinking can lead to behaviors that would never occur in a sober state. Alcohol belongs in the category of drugs called depressants, which means that drinking alcohol results in depressing, or slowing down brain processes. As a result of this alteration, alcohol abusers can behave uncharacteristically and aggressively.
Still, not all alcoholics are alike. They experience different subsets of symptoms. We do know that heavy drinking may have extensive and far–reaching effects on the brain, ranging from simple “slips” in memory to permanent and debilitating conditions that require lifetime custodial care.
And while researchers have not yet found conclusive evidence that any one variable can consistently and completely account for the brain deficits, they do know that alcohol impairs the way the brain normally works. So, a person who drinks heavily over a long period of time may have brain deficits that persist well after he or she achieves sobriety. Exactly how alcohol affects the brain and the likelihood of reversing the impact of heavy drinking on the brain remain hot topics in alcohol research today.
Is Alcoholism Treatable?
Yes.
Those who have drinking problems can solve their addiction issues with the help of health care professionals such as addiction counselor. According to studies on Alcohol Use Disorders, alcoholics requires medical help and treatment to address physical and mental aspects of the problem. Treatment helps recovering alcoholics reduce their drinking and report fewer alcohol-related problems.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to alcohol addiction problems. What might work someone, may not be a good fit for another person. This is why it is important to research all available options and chose what you think will work the best. There are various treatment options for alcohol abuse problems such as:
1. Behavioral Therapy: Lead by healthcare professionals, behavioral therapy techniques are focused on helping those addicted to alcohol in changing their behavior through counseling.
2. Medication Therapy: Three medications are currently approved in the United States to help people stop or reduce their drinking and prevent relapse:
- Disulfiram
- Naltrexone
- Acamprosate
These medications can be prescribed only by a primary care physician or a doctor and can be used alone or in combination with counseling.
3.Support Groups: Alcoholics Anonymous and other 12-step programs provide peer support for people quitting or cutting back on their drinking. Combined with treatment, mutual-support groups can be very beneficial for those who struggle with drinking issues.
So who can you see for help?
If you know someone who’s experiencing alcohol addiction issues, you can refer them to:
- Alcohol Counselor
- Licensed Psychologist and/or Psychiatrist
- Medical Doctor
- Social Worker
Here are some online resources which can help you find professional help:
- American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry (AAAP)
- American Psychological Association (APA)
- American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM)
- NAADAC Substance Abuse Professionals
- National Association of Social Workers
When in need of a treatment facility, use SAMHSA’s treatment service locator.
Obstacles to Treatment
The main thing which makes alcohol addiction so hard to address is the stigma attached to it. We think that drinking too much is a sign of weakness or a moral problem. Someone should just stop quitting if it’s hurting them, right? But a drinking problem is a medical problem.
People who are addicted to alcohol have gone through profound – and most reversible – brain changes. But you cannot underestimate how the brain changes its function when someone is drinking.
Additionally, there are huge obstacles to quitting the drinking cycle. They range from the cost of treatment to a person’s support network to the way that they feel about themselves. Here are some of the most common obstacles to successful alcohol addiction treatment:
1. Being In Denial
Denial is probably the greatest enemy to anyone’s recovery journey. False statements such as: “I can choose to stop whenever I want,” or “I can handle my drinking,” are the most commonly heard statements among alcoholics in denial. This is why a professional interventionist or addiction counselor might be the only way to break through to a loved one. Professionals are trained in messaging and planning for objection. Plus, they help pull you through during a tough time.
Accepting loss of control over alcohol consumption is not a sign of weakness. On the contrary, it is a sign of consciousness. Help can only be given to those who ask for it. So, for the alcoholic mind, realizing that they have an alcohol problem is the first step on the way to change.
2. Lack Of Devotion And Commitment
In order to really “change”, the desire to be different needs to come from inside. You cannot wish someone to be different than they are; they must want to change. So, one of the other things that can get in the way of getting better is a person’s own mindset.
Indeed, psychologists and psychiatrists say that awareness of a problem does not always signify change. Commitment during treatment are vital to be able to get through withdrawal and maintain sobriety. Recovery does not work unless an alcoholic works it: for themselves, by themselves.
3. Lack Of Good Aftercare Plan
Alcohol recovery is an ongoing process. So, treatment does not end once a person leaves rehab. The real battle begins when s/he needs to make change last. so, the transition from rehab to home should be done only after a person is adequately prepared. Sometimes, this can be months or years later. You need to understand and accept this.
The main idea here is that an aftercare plan is needed if you want to see someone change for good. This plan outlines a strategy designed to help individuals deal with all the challenges that await them. So, when they leave rehab, they are ready to return home.
Top 5 Things To Avoid When Getting Into An Alcoholic’s Mind
1. Avoid self sacrifice. You can only help an alcoholic loved one as much as they let you.
2. Avoid giving criticism; it can only lead to conflict. Your alcoholic loved one needs to recognize the problem , perhaps with support from a profession.
3. Avoid enabling your loved one alcohol addiction. Enabling a loved one’s addiction can hurt you both.
4. Avoid discussing anything with your alcoholic loved one when s/he is under the influence; they can become violent.
5. Avoid any kind of negative talk. Instead, focus on looking for treatment alternatives for yourself and your loved one.
An Extra Tip To Getting Into An Alcoholic’s Mind
The last thing you need to keep in mind regarding your loved one’s alcohol addiction problem is this: understanding more about the alcoholic brain is not going to make him/her stop. But getting to the bottom of how alcohol influences on the brain might give you more acceptance of the situation that you are currently in. Always remember that in order for an alcoholic to recover, medical help and treatment are required. The only thing you can do is be a part of your loved one’s recovery journey and give them all the support they need along the way.
Questions?
Have any more questions? We’d love to hear from you!
If you still have questions regarding getting into an alcoholic’s mind after reading this article, we welcome you to post them in the comments section. We will try to provide personal answers as quickly as we can, or refer you to someone who can help.