Eating more fruits, vegetables and nuts can make a meaningful impact on a person’s health – and the planet’s too.
Vegetarian and vegan options have become standard fare in the American diet, from upscale restaurants to fast-food chains. And many people know that the food choices they make affect their own health as well as that of the planet.
But on a daily basis, it’s hard to know how much individual choices, such as buying mixed greens at the grocery store or ordering chicken wings at a sports bar, might translate to overall personal and environmental health. That’s the gap we hope to fill with our research.
We are part of a team of researchers with expertise in food sustainability and environmental life cycle assessment, epidemiology and environmental health and nutrition. We are working to gain a deeper understanding beyond the often overly simplistic animal-versus-plant diet debate and to identify environmentally sustainable foods that also promote human health.
Building on this multi-disciplinary expertise, we combined 15 nutritional health-based dietary risk factors with 18 environmental indicators to evaluate, classify and prioritize more than 5,800 individual foods.
Ultimately, we wanted to know: Are drastic dietary changes required to improve our individual health and reduce environmental impacts? And does the entire population need to become vegan to make a meaningful difference for human health and that of the planet?
Putting hard numbers on food choices
In our new study in the research journal Nature Food, we provide some of the first concrete numbers for the health burden of various food choices. We analyzed the individual foods based on their composition to calculate each food item’s net benefits or impacts.
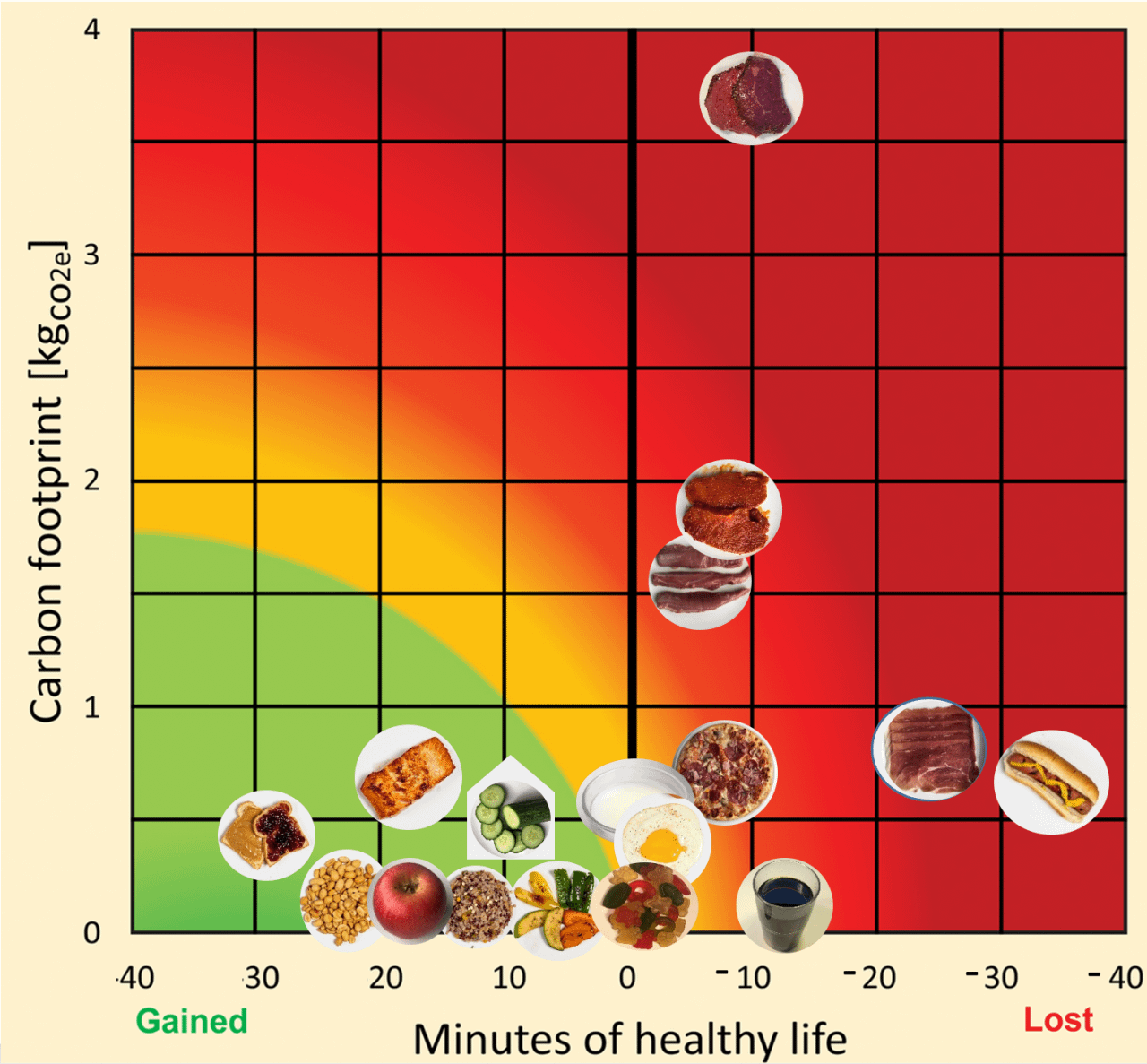
The Health Nutritional Index that we developed turns this information into minutes of life lost or gained per serving size of each food item consumed. For instance, we found that eating one hot dog costs a person 36 minutes of “healthy” life. In comparison, we found that eating a serving size of 30 grams of nuts and seeds provides a gain of 25 minutes of healthy life – that is, an increase in good-quality and disease-free life expectancy.
Our study also showed that substituting only 10% of daily caloric intake of beef and processed meats for a diverse mix of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, legumes and select seafood could reduce, on average, the dietary carbon footprint of a U.S. consumer by one-third and add 48 healthy minutes of life per day. This is a substantial improvement for such a limited dietary change.
Relative positions of select foods, from apples to hot dogs, are shown on a carbon footprint versus nutritional health map. Foods scoring well, shown in green, have beneficial effects on human health and a low environmental footprint. (Austin Thomason/Michigan Photography and University of Michigan, CC BY-ND)
How did we crunch the numbers?
We based our Health Nutritional Index on a large epidemiological study called the Global Burden of Disease, a comprehensive global study and database that was developed with the help of more than 7,000 researchers around the world. The Global Burden of Disease determines the risks and benefits associated with multiple environmental, metabolic and behavioral factors – including 15 dietary risk factors.
Our team took that population-level epidemiological data and adapted it down to the level of individual foods. Taking into account more than 6,000 risk estimates specific to each age, gender, disease and risk, and the fact that there are about a half-million minutes in a year, we calculated the health burden that comes with consuming one gram’s worth of food for each of the dietary risk factors.
For example, we found that, on average, 0.45 minutes are lost per gram of any processed meat that a person eats in the U.S. We then multiplied this number by the corresponding food profiles that we previously developed. Going back to the example of a hot dog, the 61 grams of processed meat in a hot dog sandwich results in 27 minutes of healthy life lost due to this amount of processed meat alone. Then, when considering the other risk factors, like the sodium and trans fatty acids inside the hot dog – counterbalanced by the benefit of its polyunsaturated fat and fibers – we arrived at the final value of 36 minutes of healthy life lost per hot dog.
We repeated this calculation for more than 5,800 foods and mixed dishes. We then compared scores from the health indices with 18 different environmental metrics, including carbon footprint, water use and air pollution-induced human health impacts. Finally, using this health and environmental nexus, we color-coded each food item as green, yellow or red. Like a traffic light, green foods have beneficial effects on health and a low environmental impact and should be increased in the diet, while red foods should be reduced.
Where do we go from here?
Our study allowed us to identify certain priority actions that people can take to both improve their health and reduce their environmental footprint.
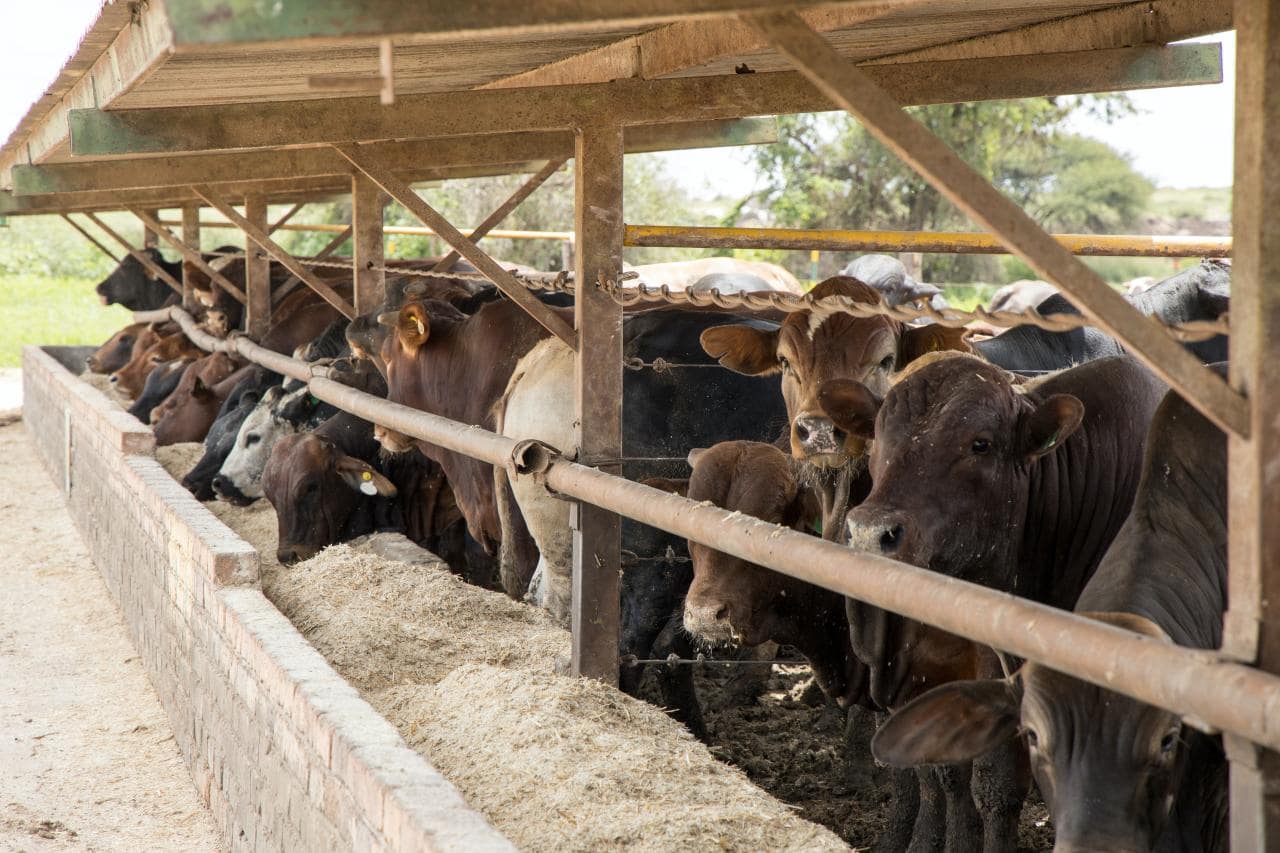
When it comes to environmental sustainability, we found striking variations both within and between animal-based and plant-based foods. For the “red” foods, beef has the largest carbon footprint across its entire life cycle – twice as high as pork or lamb and four times that of poultry and dairy. From a health standpoint, eliminating processed meat and reducing overall sodium consumption provides the largest gain in healthy life compared with all other food types.
Beef consumption had the highest negative environmental impacts, and processed meat had the most important overall adverse health effects. (ID 35528731 © Ikonoklastfotografie | Dreamstime.com)
Therefore, people might consider eating less of foods that are high in processed meat and beef, followed by pork and lamb. And notably, among plant-based foods, greenhouse-grown vegetables scored poorly on environmental impacts due to the combustion emissions from heating.
Foods that people might consider increasing are those that have high beneficial effects on health and low environmental impacts. We observed a lot of flexibility among these “green” choices, including whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, legumes and low-environmental impact fish and seafood. These items also offer options for all income levels, tastes and cultures.
Our study also shows that when it comes to food sustainability, it is not sufficient to only consider the amount of greenhouse gases emitted – the so-called carbon footprint. Water-saving techniques, such as drip irrigation and the reuse of gray water – or domestic wastewater such as that from sinks and showers – can also make important steps toward lowering the water footprint of food production.
A limitation of our study is that the epidemiological data does not enable us to differentiate within the same food group, such as the health benefits of a watermelon versus an apple. In addition, individual foods always need to be considered within the context of one’s individual diet, considering the maximum level above which foods are not any more beneficial – one cannot live forever by just increasing fruit consumption.
At the same time, our Health Nutrient Index has the potential to be regularly adapted, incorporating new knowledge and data as they become available. And it can be customized worldwide, as has already been done in Switzerland.
It was encouraging to see how small, targeted changes could make such a meaningful difference for both health and environmental sustainability – one meal at a time.
[You’re smart and curious about the world. So are The Conversation’s authors and editors. You can get our highlights each weekend.]
![]()
Olivier Jolliet, Professor of Environmental Health Sciences, University of Michigan and Katerina S. Stylianou, Research Associate in Environmental Health Sciences, University of Michigan
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.